What is Carbomer 940
introduction:
Carbomer 940 is a polymer material composed of acrylic acid and a crosslinker. Since its commercialization in the 1950s, it has gradually become a key functional ingredient in the fields of medicine, cosmetics and personal care. Its unique rheological control ability, biocompatibility and chemical inertness make it irreplaceable in complex formulation systems.
With the improvement of modern industry’s requirements for material performance, the molecular design, functional modification and green synthesis technology of Carbomer 940 have become research hotspots. Starting from the chemical essence, this paper will systematically explore its structural characteristics, mechanism of action, application scenarios and future technological trends, aiming to provide theoretical reference for the research and development and production of related fields.
Table of Contents
1.The Chemical Structure And Classification Of Carbomer 940
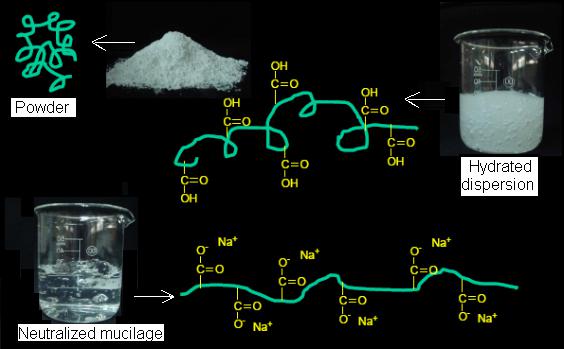
The molecular structure of Carbomer 940 is based on acrylic acid as the main chain, and forms a three-dimensional network with a crosslinker (such as allyl sucrose or pentaerythritol) through covalent bonds. The carboxylic acid group of the acrylic acid monomer provides it with pH sensitivity, while the type and proportion of the crosslinker directly determine the swelling ability and mechanical strength of the material.
According to the classification standards of the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), Carbomer is numbered as 934, 940, 941 and other different models. The difference in numbers is due to the difference in cross-linking density and molecular weight in the polymerization process. For example, Carbomer 940 has a higher degree of cross-linking and stronger inter-molecular chain forces, which is suitable for scenarios requiring high viscosity and rapid gelation; while Carbomer 941 has a lower degree of cross-linking and a looser molecular network, making it easier to disperse in low shear systems.
From the perspective of chemical stability, Carbomer 940 has strong tolerance to heat and light in a dry state, but is susceptible to oxidative degradation in a hydrated state. Its carboxylic acid group can be completely dissociated in the pH range of 6-10 to form a negatively charged polymer chain, which maintains the stability of the gel structure through electrostatic repulsion. This feature enables it to respond to changes in the microenvironment of the intestinal or skin surface in a drug sustained-release system to achieve controlled drug release.

2.Physical And Chemical Properties And Functional Mechanisms
The rheological properties of Carbomer 940 are the basis of its core functions. Its water dispersion system is a non-Newtonian fluid with significant pseudoplasticity and thixotropy. In a static state, the molecular chains form temporary crosslinking points through hydrogen bonds and van der Waals forces, which show high viscosity; when subjected to shear force, these weak interactions are destroyed, the viscosity drops rapidly, and it is easy to process or apply; after the shear force is removed, the network structure can be gradually restored, thereby ensuring the storage stability of the product. This dynamic equilibrium property enables it to provide a delicate texture in cosmetics while avoiding the sticky feeling during use.
It is worth noting that Carbomer 940 is extremely sensitive to multivalent cations (such as Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺). These ions can form complexes with carboxylates, compress the diffuse double layer, and cause molecular chain contraction and a sharp drop in viscosity. For this reason, chelating agents (such as disodium EDTA) or low cross-linking Carbomer 940 should be introduced into electrolyte-containing formulas to alleviate ion interference. At the same time, Carbomer 940 has poor compatibility with anionic surfactants and is prone to flocculation or phase separation. It is necessary to improve the system compatibility by adjusting the pH value or adding non-ionic stabilizers.
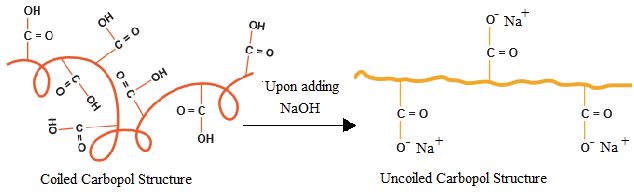
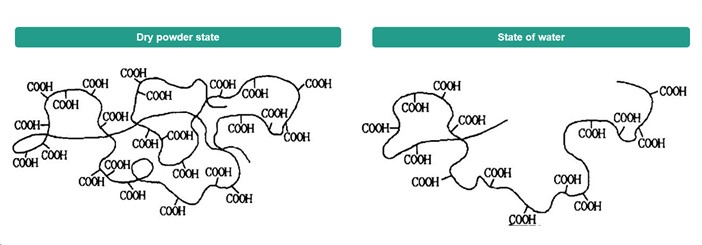
Swelling kinetics is another important property of Carbomer 940. Unneutralized Carbomer 940 powder absorbs water in water through capillary action, the carboxylic acid groups gradually ionize, and the molecular chains stretch due to charge repulsion to form a highly hydrated gel network. The swelling rate is affected by particle size distribution, crosslinking density and ambient temperature. Experiments show that the complete swelling time of Carbomer 940 powder with a particle size of less than 50 μm at 25°C can be shortened to 2-4 hours, while coarse particles may require more than 12 hours. In addition, the type of neutralizer (such as triethanolamine, sodium hydroxide) not only affects the final viscosity after swelling, but also determines the transparency and electrolyte tolerance of the gel.
3.The Industrial Application Of Carbomer 940
The Field of Medicine
In pharmaceutical preparations, Carbomer 940 is mainly used as a matrix material for topical gels, eye drops and oral suspensions. Its three-dimensional network structure can effectively encapsulate hydrophilic drugs (such as antibiotics and antifungal agents) and control the drug diffusion rate by adjusting the cross-linking density.
For example, in transdermal drug delivery systems, Carbomer 940 gel can prolong the retention time of drugs in the stratum corneum and reduce the side effects caused by systemic absorption; in ophthalmic preparations, its viscoelasticity can reduce tear wash and increase corneal contact time. In recent years, the composite system of Carbomer 940 and thermosensitive materials (such as poloxamer) has been used to develop in situ gels, which can transform from a solution to a semi-solid state under the trigger of body temperature to achieve precise drug delivery.


The Field of Cosmetics
Carbomer 940 has thickening, suspension and film-forming functions in skin care products. The gel network it forms can stabilize the emulsion system, prevent the separation of the oil phase and the water phase, and suspend active ingredients (such as antioxidants and whitening agents) to avoid precipitation.
In sunscreen products, the synergistic effect of Carbomer 940 and titanium dioxide or zinc oxide can reduce the agglomeration of inorganic particles, improve the efficiency of ultraviolet scattering, and improve the skin feel after application. In addition, Carbomer 940 is used as a conditioner in shampoo to form a protective film on the surface of hair by adsorption, reducing static electricity and frizziness.
The Field of Bioengineering
Carbomer 940’s high water content and biocompatibility make it a rising star in the field of tissue engineering and wound repair. For example, Carbomer 940 hydrogels loaded with growth factors (such as EGF or bFGF) can maintain a moist wound microenvironment and accelerate epithelial cell migration; after being compounded with antibacterial nanoparticles (such as silver nanoparticles), it can simultaneously play a physical barrier and antibacterial role.
In 3D bioprinting, Carbomer 940, as a sacrificial support material, can provide cells with a temporary growth scaffold, and can be gently removed by adjusting the pH value after molding to avoid damaging the cell structure.

4.The Preparation Method Of Carbomer 940
The industrial production of Carbomer 940 usually adopts solution polymerization. Under nitrogen protection, acrylic acid monomer, crosslinker and initiator (such as ammonium persulfate) are dissolved in an inert solvent such as benzene or cyclohexane, and free radical polymerization is initiated by heating to 60-80℃. After the reaction is completed, the solvent is recovered by distillation, and the remaining polymer is crushed and sieved to obtain a white fluffy powder.
Among the process parameters, the initiator concentration and reaction temperature have a significant effect on the molecular weight distribution: too high initiator concentration will lead to premature chain termination reaction and reduce the molecular weight; while temperature fluctuations may cause uneven crosslinking and form local “hard lumps”.
1) Weigh 1g Carbomer 940 and place it in a 50ml dry beaker. If there are lumps, please crush them with a spoon.
2) Add 25ml of pure water and stir while adding to allow Carbomer 940 to fully absorb water and swell. This step is very critical. It must be allowed to fully absorb water. Generally, after adding water and stirring, it takes a few hours for Carbomer to fully swell. If you want to speed it up, you can use a water bath to heat it. Stirring while heating will be faster. Of course, even if heating can accelerate the water absorption and swelling process of Carbomer 940, it still takes 10 to 30 minutes.
3) Use a dropper to add alkali solution, stir while adding, and measure the pH value. When the pH is adjusted to 7, the gel is successful. (Triethanolamine can be used as the alkali solution)
4) Make up the remaining water, the total volume is about 50ML.
5) The prepared gel base can be directly mixed with other raw materials to prepare various gels, as long as the carbomer concentration is controlled within 0.8%. It is recommended to be around 0.5%.
5.The Security of Carbomer 940
The toxicological data of Carbomer 940 indicate that it has a relatively high biological safety. In the acute oral toxicity test, if the median lethal dose (LD50) of rats is greater than 5,000 mg/kg, it belongs to a actually non-toxic substance. Skin irritation tests show that it has no significant irritation to intact skin, but long-term contact with broken skin may trigger a mild inflammatory response.
According to the pharmacopoeia of various countries and the specifications of cosmetic raw materials, the usage concentration of Carbomer 940 is usually limited within the range of 0.5% – 2.0%. In the drug application, detailed data on physical and chemical properties, impurity spectra and stability studies need to be provided. For cosmetic applications, they must comply with the naming and purity standards of the International Cosmetic Ingredient Dictionary (INCI). It is worth noting that the carboxylic acid group of Carbomer 940 May undergo complexation reactions with cationic surfactants (such as benzalkanium chloride), resulting in turbidity or precipitation of the system. Therefore, compatibility tests need to be conducted during formulation development.
6.Research trends of Carbomer 940
At present, the research hotspots of Carbomer 940 are concentrated on functional modification and green synthesis technology. By introducing hydrophobic chain segments (such as polylactic acid or polycaprolactone) through graft copolymerization, it can be endowed with dual response characteristics of temperature sensitivity or pH, thereby developing intelligent drug delivery systems. On the other hand, the polymerization process that uses supercritical carbon dioxide instead of traditional organic solvents can significantly reduce the emission of volatile organic compounds, which is in line with the requirements of sustainable development.
The technical challenges mainly focus on the balance between performance optimization and cost control. For example, the thickening efficiency of Carbomer 940 with a high crosslinking degree is excellent, but the dissolution time is relatively long. Although products with low crosslinking degrees are easy to disperse, they may cause the system to be unstable due to insufficient mechanical strength. Furthermore, how to enhance the ability to resist ion interference through structural design remains an urgent problem to be overcome in the industrial sector.
7.The Future Outlook of Carbomer 940
With the growth of the demands for precision medicine and personalized care, the functionalization and intelligence of Carbomer 940 will become the main development directions. By compounding with other polymers (such as chitosan, hyaluronic acid) or inorganic nanoparticles (such as silica, montmorillonite), a multifunctional gel platform can be constructed to meet high-end application scenarios such as wound healing, transdermal drug delivery and tissue engineering. Meanwhile, artificial intelligence-assisted molecular design is expected to accelerate the research and development process of new Carbomer 940 derivatives and promote their penetration in more cutting-edge fields.
References
Chemicalbook-Carbomer 940