Introduction To 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP

introduction:
4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP has become an indispensable nucleophilic catalyst in many organic synthesis reactions, becoming essential in many drug synthesis, material science and fine chemicals applications. Not only can DMAP speed up reaction times while increasing yield and purity of target product yields – it plays a pivotal role in many fields such as drug discovery.
Table of Contents
1.The Basic Properties of 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP
①.Physical properties
4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP is a white crystalline powder with an extremely small density (0.906g/cm3 at 25) at room temperature and pressure, melting point between 113℃~114℃, and boiling point at 211℃. Water solubility for DMAP is approximately 76g/L which allows it to play an essential catalytic role during aqueous phase reactions; at the same time it possesses great chemical stability allowing it to retain good activity in various organic solvents.

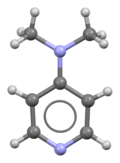
②.Chemical Properties
4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP’s chemical structure affords it unique chemical properties. Containing two electron-donating groups-dimethylamino and pyridine rings-it has strong nucleophilicity. Due to this quality, 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP performs very well as an organic catalyst, specifically in esterification, amidation, etherification, etc. reactions which require catalysis – helping significantly lower activation energy and accelerate reaction rates. Furthermore, complexes with certain metal ions further expanding its use within catalysis applications.
③. Molecular structure and characteristics
4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP’s molecular formula is C7H11N2, and its structure comprises of an electron-deficient aromatic pyridine ring and an electron-donating dimethylamino group at position 4. This design provides DMAP with several desirable characteristics:
1 Extreme Nucleophilicity: The electron-donating properties of dimethylamino groups provide significant activation of nitrogen atoms in pyridine rings, making it easy to combine with electrophilic reagents such as acyl chlorides or isocyanates.
2 High catalytic efficiency: DMAP’s catalytic efficiency in reactions such as acylation and silylation is hundreds to tens of thousands times greater than traditional catalysts (such as pyridine).
3 Stability and Compatibility: High temperature resistance (decomposition temperature > 250degC), compatible with most organic solvents such as chloroform and THF as well as metal catalysts like palladium or copper catalysts.
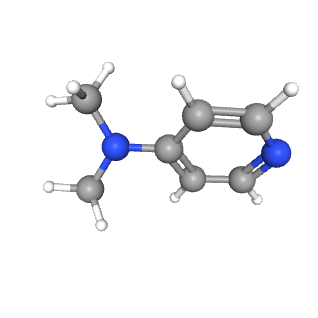
2.The Application of 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP
①.Catalytic effect
In organic chemistry, 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP is defined as a base and a basic catalyst. It is mainly used to catalyze the acylation and lactonization of sterically hindered hydroxyl groups, and is also used to catalyze the siliconization and etherification of alcohols.
The acylation of hydroxyl groups is one of the most important and frequent functional group transformation reactions in organic chemistry. In many cases, the acylation reaction can be conveniently completed using an acylating agent and an organic base or an inorganic base as an acid-binding agent. However, when there are multiple functional groups in the hydroxyl-containing substrate molecule, especially some acid- or temperature-sensitive functional groups, the reaction needs to be highly selective and carried out under mild conditions.
Because the lone pair of electrons carried by the nitrogen atom on the dimethylamino group in the DMAP molecule resonates with the aromatic ring, the nucleophilicity of the nitrogen atom on the pyridine ring is increased. Therefore, as an acylation transfer reagent, DMAP is 1000 to 1 000000 times faster than the acylation reaction catalyzed by pyridine. Generally speaking, DMAP is used as a catalyst in an amount of 0.05~0.2 mol. Most DMAP-catalyzed reactions can be completed at room temperature within minutes to hours and give very high yields (Equation 1 and Equation 2)
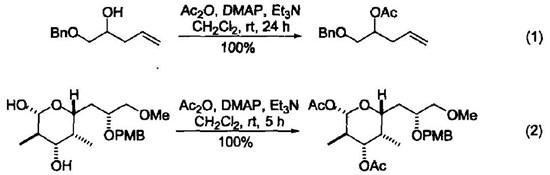
Under the catalysis of 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP, the speed and yield of the direct esterification reaction of hydroxyl groups under the action of condensation reagents are significantly improved. For complex substrate molecules, the selectivity of the reaction is also improved accordingly. This reaction is used four times in some natural product total synthesis routes (Equation 3 and Equation 4)

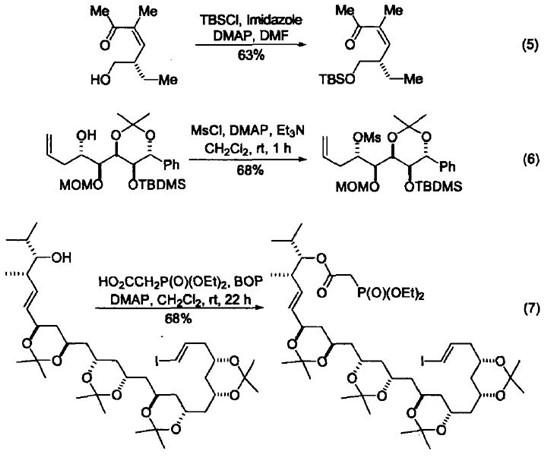
In the presence of 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP, the phosphorylation, sulfonation and silylation reactions of hydroxyl groups all have significant catalytic effects. Therefore, many reactions that cannot be completed under normal reaction conditions or the protective groups will be damaged give satisfactory results under these conditions. (Equation 5 ~ Equation 7)
②.Applications in the Field of Polymers
4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP plays an essential role in the polymer materials industry. Used as a catalyst for polycondensation between isocyanates and polyols, DMAP can effectively inhibit formation of by-products like urea bonds while simultaneously encouraging linear polymer chain growth – which enhances mechanical properties like tensile strength and elastic modulus while shortening curing times considerably and decreasing production energy costs.
DMAP can also enhance the curing process of epoxy resin systems through its catalytic properties: its latent catalyst properties remain inactive at room temperature but release alkaline active sites when heated above 120degC, initiating polymerization processes by opening up epoxy groups ring-opening polymerization. Due to this controllable curing property it finds widespread usage across electronic packaging materials, composite materials and other fields.


③.In the Field of Analysis
4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP’s most prominent application in analytical chemistry lies in its derivatization capabilities. DMAP forms derivatives with strong ultraviolet absorption or fluorescence properties from carboxylic acid compounds, thus improving detection sensitivity using liquid chromatography (HPLC) or capillary electrophoresis.
DMAP can reduce fatty acid analysis detection limits to ppb level, making it significantly better than conventional derivatization reagents. Furthermore, DMAP is also an auxiliary reagent used for chiral separation by forming hydrogen bonds or p-p interactions with non-polar compounds, optimizing separation of enantiomers through chromatographic columns; an essential feature in drug purity control and optically active substances analysis.
④.The Field of Medicine
4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP plays an integral part in drug research and production chains from intermediate synthesis through final product modification, from side chain introduction and protective group operations for antibiotics (such as cephalosporins and penicillins) to playing an instrumental catalytic function for antitumor drugs ( such as paclitaxel derivatives) and cardiovascular drugs ( such as statins).
DMAP’s high efficiency can be directly tied to its cost control for drug production: by decreasing reaction steps and catalyst amounts used and improving purity levels of their product, they can significantly decrease purification costs while improving batch stability.


⑤.In the Field of Pesticides
4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP has proven its effectiveness in pesticide application as well, with remarkable results in this sector. It can synthesize various pesticides like pyrethroid insecticides, carbamate insecticides and amide herbicides; and as global agriculture progresses and increased demand for more eco-friendly solutions increases, DMAP plays an essential role in upgrading the industry through improving production efficiency and quality, developing low toxic products that support food security as well as ecological environmental balance.
3.The Preparation Method of 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP
①.Direct amination method
Raw materials: 4-chloropyridine, dimethylamine
Reaction process: Starting with pyridine and phosphorus trichloride as raw materials, they are first combined together to generate 4-chloropyridine; later this 4-chloropyridine mixture is heated under normal pressure reflux for five hours under sodium methoxide catalysis; finally DMAP can be purified via vacuum distillation to produce yields between 50%-55%.
Key points of the process:
Catalyst selection: Copper salts such as CuCl2 can facilitate chlorine atom substitution quickly, with yield exceeding 70%.
Byproduct treatment: Any generated hydrogen chloride must be neutralized with alkaline solutions like NaOH in order to avoid equipment corrosion.
Purification process: After recrystallizing, the crude product can reach 99.5% purity with this process.
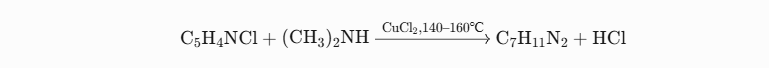
②.The 4-Cyanopyridine Method
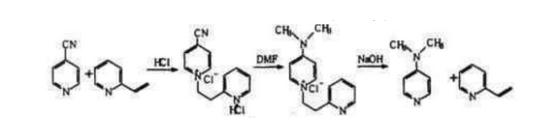
Raw materials:4-Cyanopyridine,Dimethylamine
Reaction process: Using 4-cyanopyridine as its starting material, this reaction method involves first quaternizing it with 2-vinylpyridine to produce an intermediate substance before reacting with dimethylamine and treating with alkali to finally obtain 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP as its target compound.

③.The Pyridine Method
Raw materials:Pyridine,Dimethylamine
Reaction process: DMAP can be prepared in two steps from pyridine by first oxidizing it to 4-pyridylpyridinium cation and reacting it with dimethylamine.
4.The Advantages of 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP
Compared with traditional alkaline catalysts, the core advantage of 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP is first reflected in its extremely high catalytic efficiency. Take the acylation reaction as an example. The catalytic activity of DMAP can reach 10⁴ times that of pyridine. This means that under the same reaction conditions, the dosage of DMAP can be reduced to less than 1% of the stoichiometric level, while the reaction time can be compressed from several hours to several minutes. This efficiency advantage is transformed into significant economic benefits in industrial production: shortened equipment occupancy time, reduced energy consumption, and increased unit production capacity. It is particularly suitable for large-scale continuous production systems.
4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP stands out as a leader in its ability to control select sites through selective activation via synergistic effects of steric hindrance and electronic effects in multifunctional substrate reactions. DMAP can be used in the acetylation reaction of polyhydroxy compounds (such as sugar derivatives ), where primary hydroxyl groups are preferentially catalyzed while secondary ones are effectively blocked, increasing regioselectivity to over 95%. Furthermore, for the synthesis of chiral compounds DMAP forms diastereomeric complexes with substrates which alter stereochemical pathways during reactions; providing new strategies to generate optically pure substances.
In terms of process adaptability, 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP exhibits strong environmental compatibility. Its catalytic activity has low sensitivity to water and oxygen, and some reaction systems can even tolerate the presence of trace amounts of water, greatly reducing the dependence on inert atmospheres in industrial production.Furthermore, its stability at room temperature simplifies storage and transportation conditions while its good compatibility with organic solvents such as THF, DMF and acetonitrile makes adjusting it to various reactions simple and expeditious – quickly adapting itself to diverse production needs quickly.
From the perspective of sustainability, the application of DMAP conforms to the development trend of green chemistry. The amount of catalytic stage used significantly reduces the overall consumption of reagents, while the high reaction efficiency lowers energy input and waste emissions. In recent years, the recycling of catalysts through imloading technology (such as loading DMAP onto silica or polymer carriers) has further enhanced their environmental value: Experimental data shows that the loaded DMAP can still maintain over 85% of its catalytic activity after being reused five times, which has dual significance for reducing production costs and solid waste generation.
Finally, the technological scalability of DMAP provides a guarantee for its continuous leading position in the market. In novel reaction systems (such as photocatalysis and electrochemical synthesis), DMAP can serve as an electron transfer medium or auxiliary catalyst; In the field of bio-based material synthesis, DMAP has demonstrated highly efficient catalytic potential for lignin and cellulose derivatives. In the context of intelligent manufacturing, the parameter sensitivity of the DMAP reaction system enables it to be deeply integrated with Process Analysis technology (PAT) to achieve real-time monitoring and dynamic optimization. This multi-dimensional technical compatibility ensures that DMAP continues to occupy a strategic position in the upgrading of the chemical industry.
5.Precautions of 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP
4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP should be stored in a cool, dry and well-ventilated environment, and avoid contact with acidic substances, strong oxidants, etc. The packaging materials should be selected from those that can isolate air and moisture, such as glass bottles or metal cans, and they should be stored in a sealed manner. At the same time, it should be noted that the storage temperature should not be too high. Generally, it is recommended to store it below 25℃.
Precautions When Applying 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP Operators using DMAP must wear appropriate protective equipment, including gloves, goggles and masks, in order to prevent it from coming in contact with skin, eyes or respiratory tract. Because DMAP can cause skin irritation if accidentally inhaled, rinse with plenty of water immediately and seek medical advice immediately if accidental contact does occur. Furthermore, reaction conditions including temperature, pressure and reaction time must be strictly managed during its production in order to guarantee its smooth progression and ensure product quality.
The waste of 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP should be disposed of in accordance with the regulations for the handling of hazardous chemicals. It must not be discharged or dumped at will to avoid causing pollution to the environment. Generally, professional methods such as chemical oxidation and incineration can be adopted for treatment to convert it into harmless substances before discharge.
6.Safety Regulations of 4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP
4-Dimethylaminopyridine DMAP is subject to stringent legal and regulatory scrutiny during its production, storage, transportation and use processes. As part of their production process, enterprises should adhere to applicable safety production regulations, ensure production facilities meet safety standards, and offer operators training in safety practices. Storage and transport operations should adhere to management regulations for hazardous chemicals, with appropriate packaging materials and transportation methods chosen to prevent leakage and accidents. Furthermore, using DMAP should adhere to relevant industry standards and operational norms to ensure its legal and safe implementation.
References
Chemicalbook-4-Dimethylaminopyridine
